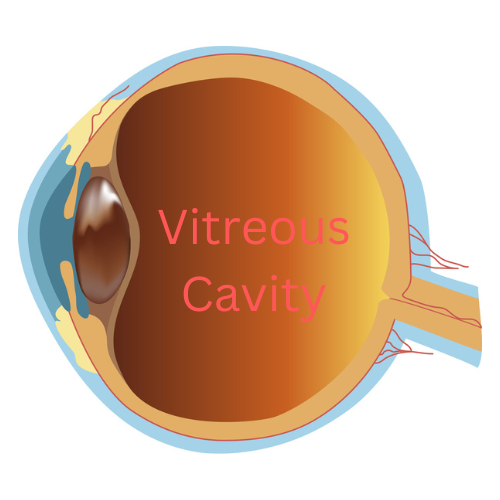
The vitreous, also known as the vitreous humor, is a gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye, occupying the space between the lens and the retina. It plays a crucial role in the development of the eye and in supporting the overall structure of the eye after we are born.
Composed mainly of water, the vitreous humor is a transparent, colorless gel that consists of a network of collagen fibers and various other molecules. It is synthesized during the early stages of development and persists throughout life. It is not renewed.
Function
The primary function of the gel is to provide mechanical support to the eyeball. It helps maintain the spherical shape of the eye, which is essential for proper focusing of light onto the retina. Additionally, the vitreous acts as a shock absorber, protecting the delicate structures within the eye from external forces or impact.
Moreover, this clear gel plays a role in the optical system of the eye. By virtue of its transparency, it transmits light, allowing it be focused on the retina. The retina converts light into electrical signals that are then transmitted to the brain, thus creating “vision.” The smooth, uniform consistency of the vitreous helps to ensure that light rays are not scattered or distorted as they travel through the eye.
Posterior Vitreous Detachment
While the vitreous is mostly a stable, gel-like substance, it can undergo changes that can impact vision. With age, the vitreous may gradually shrink and develop small pockets of fluid. This is known as a posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). This can lead to the formation of floaters, which are perceived as tiny specks or threads that seem to float across the field of vision. Although floaters are usually harmless, a sudden onset of numerous floaters or flashes of light may be a sign of a retinal tear. A retinal tear can cause a retinal detachment, which requires immediate medical attention. Sudden onset of floaters should always be checked by your eye doctor.
The vitreous is most important for normal development of the eye. Once we are born, it indirectly maintains various functions of the retina and the lens. Understanding the role of the vitreous can help appreciate its importance in maintaining healthy vision and identifying potential eye problems.
If you would like to schedule an appointment, please call us (877) 245.2020.